Table of Contents
- What is the Google SERP?
- Birth and evolution of Google SERPs
- Type of content in a Google SERP
- How much do structured data count in a Google search results page?
- The importance of Google SERPs for SEO
What is the Google SERP?
What is the SERP? It stands for Search Engine Results Page, which in Italian is translated as ‘Pagina dei Risultati del Motore di Ricerca‘.
It is the web page displayed by a search engine when a user performs an online search.
For seo consultants, it is important to place the pages they take care of on the first page and, above all, in the first results.
The SERP contains a list of results relevant to the search query entered by the user.
This is an important visualisation for SEO as the SEO expert works precisely to place the sites he deals with in the highest places on this page.
Birth and evolution of Google SERPs
Here is an overview of the evolutionary history of Google’s SERP:
- Early 2000s: Simple Layout In the early 2000s, Google’s SERP had a very simple layout with organic results and a few advertisements. The results were mainly textual, with titles, descriptions and URLs.
- Introduction of Google AdWords: In 2000, Google launched Google AdWords, its pay-per-click (PPC) advertising programme, which introduced paid advertisements in the SERP These announcements were clearly marked as ‘Announcements’.
- Universal Search (2007): In 2007, Google introduced the concept of Universal Search, which integrated different types of results on the same page, including videos, images, news and more. This enriched the research experience with multimedia content.
- Google Instant (2010): In 2010, the Google Instant function was introduced, which showed search results in real time as the user typed in the query. This feature was intended to make searches faster and more intuitive.
- Knowledge Graph (2012): In 2012, Google launched Knowledge Graph, a system that understands the relationships between different entities and offers contextual information directly on the SERP. For example, if you search for a famous person, biographical information is displayed in the right-hand pane.
- Mobile-Friendly Layout (2015): Google made mobile-friendly design a priority by introducing an algorithm that favours mobile-optimised sites in mobile searches.
- Featured Snippets (2014-2017): Google began displaying ‘Featured Snippets’ or foreground boxes, which are portions of text extracted from web pages that respond directly to user queries.
- BERT (2019): In 2019, Google introduced BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), an advanced natural language understanding algorithm to better understand the context of user queries.
- Renewed Results Page (2020): In 2020, Google made significant changes to the SERP layout, redesigning the font and making the organic results and ads more prominent.
Google’s SERP continues to evolve with the introduction of new features, algorithms and designs to improve the search experience for users.
Type of content in a Google SERP
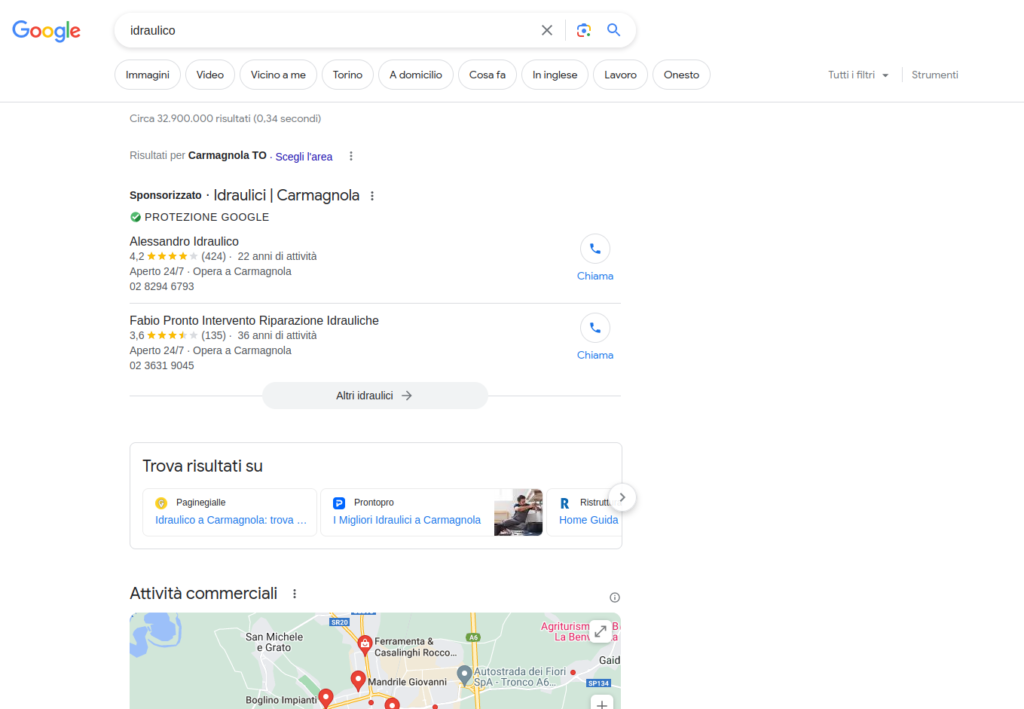
These results may include different types of content, including:
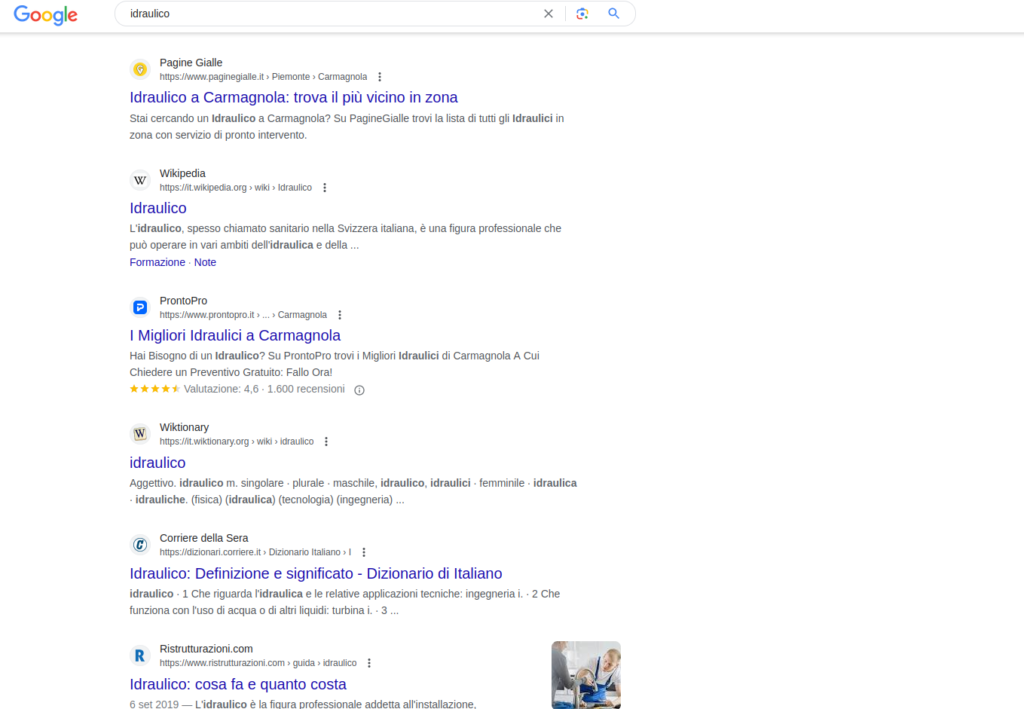
Organic results
These are the ‘natural’ and not paid search results. They are generated by search engine algorithms based on relevance to the keywords searched for by the user. The website URLs and descriptions related to the organic results are listed on the main results page.
The snippet of an organic result usually consists of the logo (favicon) of the linked site, the breadcrumb of the page, the title (title meta tag) the description (meta description), any other links (sitelinks), any rating and number of reviews.
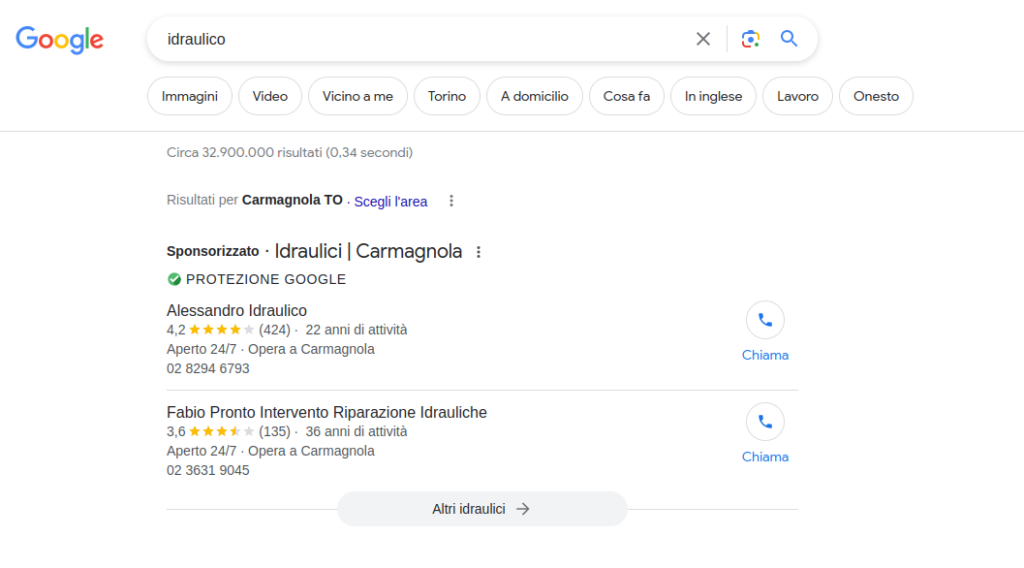
Sponsored announcements
These results are paid for by advertisers to be displayed at the top or side of the SERP. Sponsored advertisements are marked as such and are usually highlighted in some way to distinguish them from organic results.
Featured Snippet
These are text fragments from a web page that directly answer the user’s question without requiring a click on the result. Featured rich snippets may appear in special boxes or prominent positions within the SERP.
They are almost always shown in first position or in the so-called ‘Google Golden Triangle’.
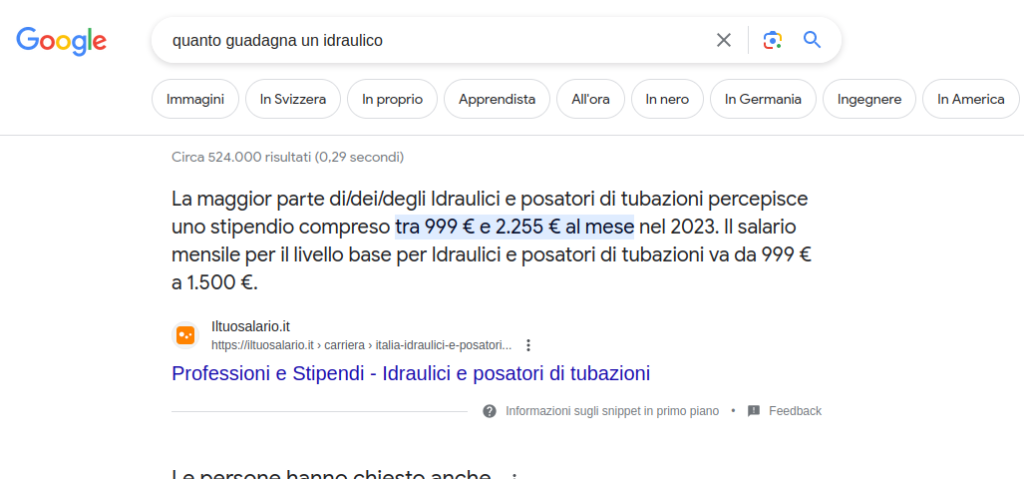
Direct answer box
These are special boxes that show direct and immediate information to common questions.
For example, a SERP might show a direct response box with the weather forecast for a specific location.
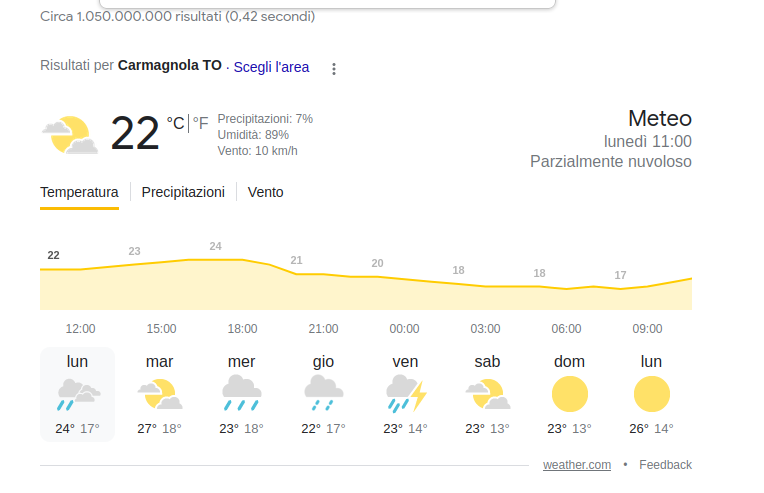
Direct response box with calculator function
When asking Google to do a mathematical operation, a direct answer box appears with calculator functions that can be used directly on the SERP page for further operations.
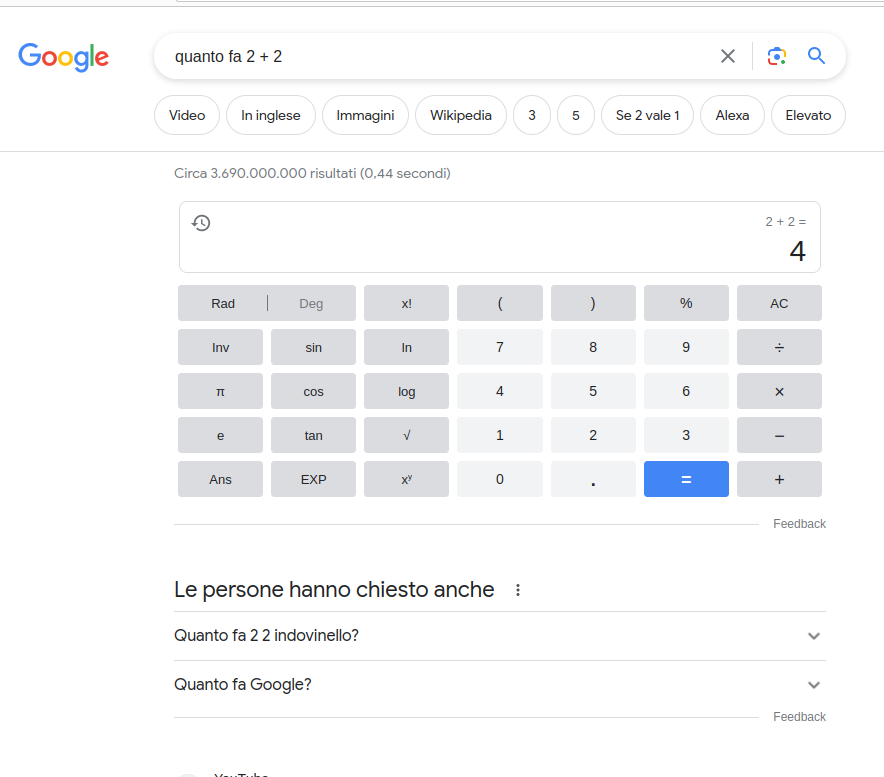
Boxes of ‘People also asked’
These boxes contain questions related to the research topic and their answers. They can be useful to obtain further information on the subject.
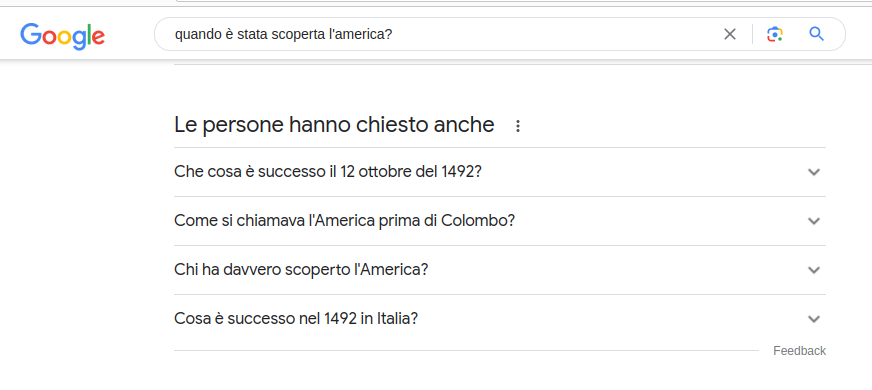
Local results
If the search has a geographical component, the SERP might show a map and results related to local places or activities.
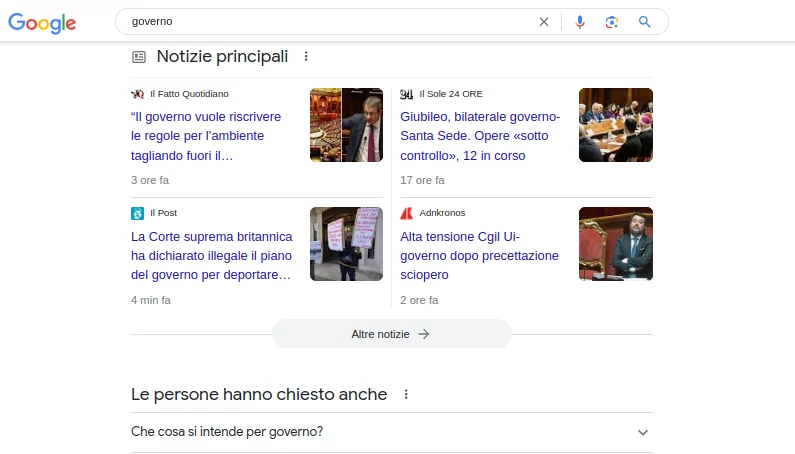
Top News
News in the Google SERP is presented as a distinctive box showing the latest news articles related to the user’s search query. This box is often placed at the top of the search results page, providing users with quick and direct access to the latest and most relevant news.
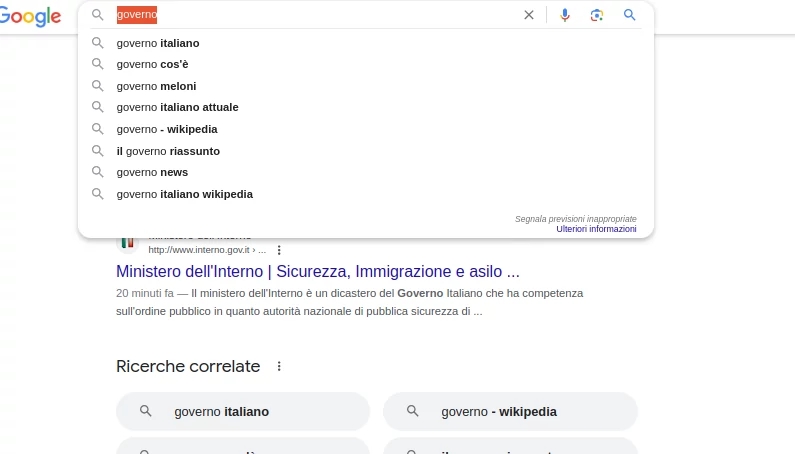
Related Searches
Related searches’ in Google’s SERP are a set of search suggestions that appear at the bottom of the search results page. These suggestions are designed to help users further refine their search query or explore related topics.
From the desktop, related searches can also be found in the search field. Simply click the mouse in the search bar and related searches will appear. A tool in the bottom right-hand corner allows ‘inappropriate predictions’ to be reported.
The composition and layout of a SERP may vary in other search engines (e.g. Google, Bing, Yahoo) and to the specific search query made.
Users choose the results they consider most relevant to their needs and click on them to obtain further information or visit relevant websites. Therefore, the SERP plays a crucial role in the online search experience of users.
How much do structured data count in a Google search results page?
Structured data, implemented through schema markup, play a significant role in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages). Structured data provide machines, including search engines such as Google, with a deeper understanding of the content of web pages.
Here is how structured data influence SERPs:
- Improved Visualisation: The implementation of structured data can improve the visualisation of search results. For instance, enriched snippets may appear, such as recipe lists, product reviews with star ratings and prices, opening hours of local businesses, events, etc.
- Featured Snippets: Google uses structured data to identify content that can be presented in Featured Snippets. Structuring content clearly and using structured data related to FAQs, Q&As or How-tos can improve the chances of being highlighted.
- Rich Results: Structured data allow the creation of rich results that include detailed information, such as recipes with nutritional ratings or events with specific dates and locations.
- Knowledge Graph: Google uses structured data to feed the Knowledge Graph, which is a knowledge base that provides information directly in the SERP.
- Local SEO: For local activities, structured data are crucial. The use of schema markup such as LocalBusiness, LocalBusinessAddress, and LocalBusinessHours helps provide clear information on locales to local searches.
- Enhanced Search Appearance: The correct implementation of structured data can lead to an enriched search appearance, with results that include images, ratings, prices and other relevant information.
- Events: For events, the use of schema markup such as Event can cause event information to be displayed in greater detail in SERPs.
- FAQ: The use of schema markup for FAQs can lead to snippets that directly answer users’ questions.
- Products: For e-commerce sites, the implementation of schema markup for products can help display information such as prices, availability, ratings and more in SERPs.
- Mobile compatibility: Structured data can improve the appearance and usability of search results on mobile devices by providing clear and well-structured information.
In summary, structured data is a powerful SEO tool that can enrich the presentation of search results and improve the understanding of content by search engines, contributing to a better user experience.
The importance of Google SERPs for SEO
Google’s SERP (Search Engine Results Page) is of crucial importance for SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) for several reasons:
- Online Visibility: The SERP is where users search for information online. Having a prominent presence in the SERP increases the visibility of one’s own website and related pages.
- Organic Positioning: Obtaining high positions in SERPs through organic results is one of the main goals of SEO. Unpaid organic results are often considered more authoritative by users.
- User Trust: Websites positioned at the top of the SERP often gain more trust from users. Users tend to believe that the results at the top are more relevant and reliable.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The position in which a site appears in the SERP affects the CTR. Results at the top generally receive more clicks than those at the bottom, which can increase traffic to your site.
- Featured Snippets: Featured snippets, such as Rich Snippets, allow key information to be presented prominently in SERPs, attracting users’ attention and improving the likelihood of clicks.
- Search Intent: The SERP reflects the search intentions of users. Understanding what types of results appear for certain queries helps to create content that meets the needs of users.
- Online Competition: Analysing the SERP allows you to assess your online competition. Understanding which sites compete for certain queries is essential for developing an effective SEO strategy.
- Local SEO: For local searches, the SERP is crucial. Having a good presence in the local SERP is crucial for attracting local customers.
- Optimisation Tools: SEO optimisation tools often focus on SERP position. Monitoring changes in ranking helps to evaluate the effectiveness of SEO strategies.
- Search Trends: Observing trends in SERPs provides valuable information on users’ search behaviour and evolutions of Google’s algorithm.
In summary, the SERP is the main battleground for online visibility, and optimising for a quality presence is crucial for SEO success.
Sign up for the newsletter. Stay updated!
We will send you periodical important communications and news about the digital world. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the appropriate link at the bottom of the newsletter.


Leave a Reply